ResNet论文+复现
ResNet(Residual Network)由何恺明等人于2015年提出(论文《Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition》),是深度学习领域里程碑式的论文。其核心思想是残差连接,解决了训练极深神经网络时遇到的退化问题。
这是ResNet论文的地址:Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
一、论文核心总结
核心问题:退化问题
- 传统的深度神经网络(如VGG)随着层数的增加(例如超过20层),在训练集和测试集上的性能反而会下降。
- 这不是由过拟合引起的(因为训练误差也升高了),也不是由梯度消失/爆炸引起的(通过BN层等技术基本解决了)。
- 这表明更深层的网络更难优化,简单地堆叠更多层并不能自动带来性能提升。
核心解决方案:残差学习
不再让网络层直接学习目标函数
H(x),而是学习残差函数F(x) = H(x) - x。目标函数因此变为
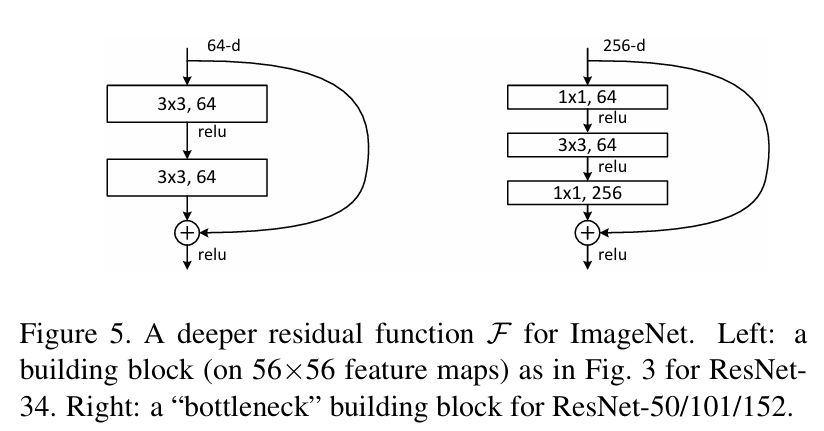
H(x) = F(x) + x。关键结构:残差块:
- 输入
x直接通过一个“快捷连接”传递到输出附近。 - 堆叠的几层非线性层学习残差映射
F(x)。 - 块的输出是
F(x) + x。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9# 伪代码表示核心残差块
def ResidualBlock(x):
identity = x # 保存原始输入 (快捷连接)
out = Conv2D(x) # 一些卷积层、BN层、激活函数等
out = ReLU(BN(Conv2D(out)))
out = ... # 可能有多层
out = out + identity # 核心操作:残差连接 (F(x) + x)
out = ReLU(out) # 最后的激活函数
return out- 输入
残差学习的优势
- 解决退化问题: 如果恒等映射
x是最优的(即更深层什么也不做最好),学习F(x) = 0比学习F(x) = x要容易得多。残差块可以轻松地学习到恒等映射(将权重推向0即可),避免了性能下降。 - 缓解梯度消失: 梯度可以通过快捷连接几乎无损地直接回传到更浅的层,极大地改善了反向传播的效率,使训练数百甚至上千层的网络成为可能。
- 提高优化效率: 残差函数通常是小幅度的扰动,相对于学习完整的映射更容易优化。
- 促进信息流动: 快捷连接提供了信息传递的高速公路。
- 解决退化问题: 如果恒等映射
关键技术点
- 快捷连接: 核心是恒等映射 (
y = x + F(x))。当输入输出维度不匹配时(例如下采样时),论文采用:- 在
F(x)路径上用步长为2的卷积进行下采样。 - 在快捷连接上用步长为2的1x1卷积进行下采样和通道数调整(
projection shortcut)。
- 在
- 瓶颈设计: 为了降低计算复杂度,在深层网络中使用了“瓶颈”残差块(1x1 Conv 降维 -> 3x3 Conv -> 1x1 Conv 升维)。这大大减少了参数数量和计算量。
- 后激活: 原始论文中,残差块内采用“后激活”模式(Conv -> BN -> ReLU),最后的相加操作后还有一个ReLU。
- 快捷连接: 核心是恒等映射 (
主要贡献与影响
- 彻底解决了深度网络的退化问题: 成功训练了高达152层(ImageNet)甚至1000层(CIFAR-10)的网络。
- 显著提升性能: 在ImageNet分类、COCO目标检测等多项计算机视觉基准任务上取得了当时最优结果。ResNet-152在ImageNet top-5错误率降至3.57%,首次超越人类水平(约5%)。
- 成为基础架构: ResNet及其变种(如ResNeXt, Wide ResNet, ResNet in ResNet, DenseNet等)成为计算机视觉乃至其他深度学习领域最广泛使用和构建的基础网络架构之一。
- 启发性强: “残差学习”的思想被广泛应用到各种网络结构(如Transformer中的残差连接)和任务中。
一句话总结核心:
ResNet 通过引入残差块(输出 = F(x) + x),利用快捷连接让网络层专注于学习输入与期望输出之间的残差F(x),而非完整的映射,有效解决了极深神经网络的退化问题,使训练成百上千层的网络成为可能,并大幅提升了模型性能。
其简单、通用且极其有效的设计,使其成为深度学习发展史上最重要的基石之一。
二、复现(CIFAR10数据集)
1 残差连接块
1 | |
2 瓶颈连接块
1 | |
3 残差网络
残差网络复现主要是根据下图进行
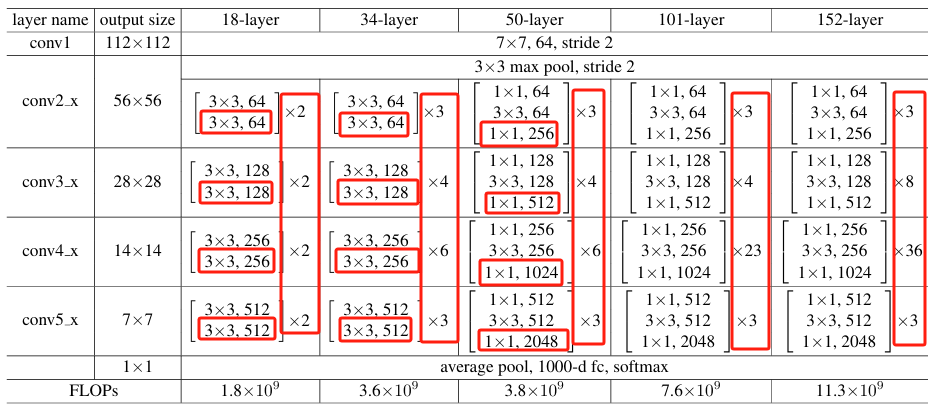
18层残差网络
1 | |
34层残差网络
1 | |
50层残差网络
1 | |
101层残差网络
1 | |
152层残差网络
1 | |
4 数据集预处理
1 | |
5 定义训练函数
1 | |
6 训练
1 | |
ResNet论文+复现
http://example.com/2025/07/25/ResNet论文/